|
gm. Cedry Wielkie, pow. gdański, woj. pomorskie
Until 1945, Käsemark TK (Endersch, Schrötter) Kaesemarck (Gotha),
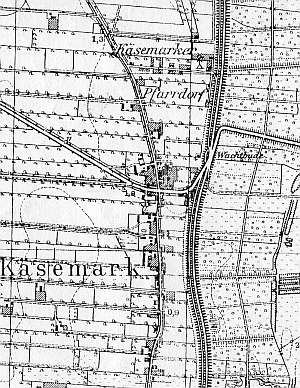
Kiezmark was an old Slavic settlement. It was granted the Chełmno rights in 1349 by the Grand Master Has Dusemer. Between 1454 and 1793 (second partition of Poland) it belonged to the city of Gdańsk. In 1820, the village had 481 residents including 6 Mennonites. Village layout - linear village in the southern section with a church surrounded by a cemetery between the street and the Vistula flood bank and marsh row village/linear village in the northern section. The village was divided into two sections by the highway no. 7 and a high embankment leading to the bridge across the Vistula. The northern section of the village with dispersed buildings has partially survived. The cultural landscape of the southern section is in better condition. In addition to a half-timbered parish church from 1727 surrounded by a cemetery with old trees and several preserved gravestones, there are 7 wooden and 5 masonry historical buildings.
 No. 33 (39) is a house situated on the western side of the
road across from the church. It was erected in 1844 on a stone
underpinning. The building has a corner-notched log structure with covered
quoins and vertically boarded gables. The interior has a two-bay layout
with wider eastern bay, the large room in the southeastern corner, a
centrally located black kitchen, and a hallway separating the rooms in the
northern section of the house. The ridge elevation has 6 axes with an
entrance in the 3rd axis from the south. The gable elevation has 3 axes,
2-axial gable, and a semicircular skylight in the finial. The building is
in very poor condition. No. 33 (39) is a house situated on the western side of the
road across from the church. It was erected in 1844 on a stone
underpinning. The building has a corner-notched log structure with covered
quoins and vertically boarded gables. The interior has a two-bay layout
with wider eastern bay, the large room in the southeastern corner, a
centrally located black kitchen, and a hallway separating the rooms in the
northern section of the house. The ridge elevation has 6 axes with an
entrance in the 3rd axis from the south. The gable elevation has 3 axes,
2-axial gable, and a semicircular skylight in the finial. The building is
in very poor condition.
 No. 21 is a former inn situated on the
Vistula flood bank, facing the road running on the flood bank with its
ridge. The building was erected ca. 1880-90. It is a one-storey building
with a pointing sill. The building has a vertically boarded log structure,
a 5-axial ridge elevation with a centrally located entrance. The gable
elevation has 3 axes, a two-level gable with two windows (lower section)
enclosed by triangular small windows, two narrow windows enclosed by
triangular shapes above, wind ties with a pazur, and notched purlin ends
resting on a notched support. No. 21 is a former inn situated on the
Vistula flood bank, facing the road running on the flood bank with its
ridge. The building was erected ca. 1880-90. It is a one-storey building
with a pointing sill. The building has a vertically boarded log structure,
a 5-axial ridge elevation with a centrally located entrance. The gable
elevation has 3 axes, a two-level gable with two windows (lower section)
enclosed by triangular small windows, two narrow windows enclosed by
triangular shapes above, wind ties with a pazur, and notched purlin ends
resting on a notched support.
 No. 59 is a house from a Dutch
homestead located in the northeastern section of the colony, on the
northern side of the road facing it with a ridge. Outbuildings have been
demolished. The house dates from the mid 1800s. It has a log structure
with covered quoins, vertically boarded gables, and a 6-axial ridge
elevation with an entrance in the 3rd axis from the east. The gable
elevation has 2 axes and a 3-axial gable with a rectangular window
enclosed by small rectangular windows. The building is in poor
condition. No. 59 is a house from a Dutch
homestead located in the northeastern section of the colony, on the
northern side of the road facing it with a ridge. Outbuildings have been
demolished. The house dates from the mid 1800s. It has a log structure
with covered quoins, vertically boarded gables, and a 6-axial ridge
elevation with an entrance in the 3rd axis from the east. The gable
elevation has 2 axes and a 3-axial gable with a rectangular window
enclosed by small rectangular windows. The building is in poor
condition.
 No. 49 is a house situated in the northern section of
the colony, on the eastern side of the road, facing it with its ridge. It
is a wooden 1.5-storey building dating from ca. 1880. It rests on a high
stone underpinning. The ground floor and an attic room have a
corner-notched log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating
pilaster, while the pointing sill (horizontal planking) and gables
(vertical planking) have a half-timbered structure. The building has a
wooden porch in front of the entrance and a queen post - collar tie roof
structure with an angle brace, and a ceramic roof. The interior has a
two-bay layout (uneven tracts) with a centrally located black kitchen, an
L-shaped hallway, which separates 3 rooms in the northern part of the
house. The gable elevation has 4 axes, a two-level gable with two
rectangular windows enclosed by two rectangular skylights bound by
triangular shapes, and two narrow windows with triangular shapes above.
The western elevation has 7 axes and a shallow 3-axial projection with a
centrally located entrance with a porch. The porch has a rich fretwork
decoration. The pointing sill has small rectangular windows in the axis of
the ground floor windows. There are also two windows in the attic room.
The building is richly decorated with carved planking, a cornice, notched
beams, and original window and door frames. There also is an old
granary/coach house in the yard. No. 49 is a house situated in the northern section of
the colony, on the eastern side of the road, facing it with its ridge. It
is a wooden 1.5-storey building dating from ca. 1880. It rests on a high
stone underpinning. The ground floor and an attic room have a
corner-notched log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating
pilaster, while the pointing sill (horizontal planking) and gables
(vertical planking) have a half-timbered structure. The building has a
wooden porch in front of the entrance and a queen post - collar tie roof
structure with an angle brace, and a ceramic roof. The interior has a
two-bay layout (uneven tracts) with a centrally located black kitchen, an
L-shaped hallway, which separates 3 rooms in the northern part of the
house. The gable elevation has 4 axes, a two-level gable with two
rectangular windows enclosed by two rectangular skylights bound by
triangular shapes, and two narrow windows with triangular shapes above.
The western elevation has 7 axes and a shallow 3-axial projection with a
centrally located entrance with a porch. The porch has a rich fretwork
decoration. The pointing sill has small rectangular windows in the axis of
the ground floor windows. There are also two windows in the attic room.
The building is richly decorated with carved planking, a cornice, notched
beams, and original window and door frames. There also is an old
granary/coach house in the yard.
KZSwP, s. 12 - 15; Lipińska,t.3- 6; AG
|

 No. 33 (39) is a house situated on the western side of the
road across from the church. It was erected in 1844 on a stone
underpinning. The building has a corner-notched log structure with covered
quoins and vertically boarded gables. The interior has a two-bay layout
with wider eastern bay, the large room in the southeastern corner, a
centrally located black kitchen, and a hallway separating the rooms in the
northern section of the house. The ridge elevation has 6 axes with an
entrance in the 3rd axis from the south. The gable elevation has 3 axes,
2-axial gable, and a semicircular skylight in the finial. The building is
in very poor condition.
No. 33 (39) is a house situated on the western side of the
road across from the church. It was erected in 1844 on a stone
underpinning. The building has a corner-notched log structure with covered
quoins and vertically boarded gables. The interior has a two-bay layout
with wider eastern bay, the large room in the southeastern corner, a
centrally located black kitchen, and a hallway separating the rooms in the
northern section of the house. The ridge elevation has 6 axes with an
entrance in the 3rd axis from the south. The gable elevation has 3 axes,
2-axial gable, and a semicircular skylight in the finial. The building is
in very poor condition. No. 21 is a former inn situated on the
Vistula flood bank, facing the road running on the flood bank with its
ridge. The building was erected ca. 1880-90. It is a one-storey building
with a pointing sill. The building has a vertically boarded log structure,
a 5-axial ridge elevation with a centrally located entrance. The gable
elevation has 3 axes, a two-level gable with two windows (lower section)
enclosed by triangular small windows, two narrow windows enclosed by
triangular shapes above, wind ties with a pazur, and notched purlin ends
resting on a notched support.
No. 21 is a former inn situated on the
Vistula flood bank, facing the road running on the flood bank with its
ridge. The building was erected ca. 1880-90. It is a one-storey building
with a pointing sill. The building has a vertically boarded log structure,
a 5-axial ridge elevation with a centrally located entrance. The gable
elevation has 3 axes, a two-level gable with two windows (lower section)
enclosed by triangular small windows, two narrow windows enclosed by
triangular shapes above, wind ties with a pazur, and notched purlin ends
resting on a notched support. No. 59 is a house from a Dutch
homestead located in the northeastern section of the colony, on the
northern side of the road facing it with a ridge. Outbuildings have been
demolished. The house dates from the mid 1800s. It has a log structure
with covered quoins, vertically boarded gables, and a 6-axial ridge
elevation with an entrance in the 3rd axis from the east. The gable
elevation has 2 axes and a 3-axial gable with a rectangular window
enclosed by small rectangular windows. The building is in poor
condition.
No. 59 is a house from a Dutch
homestead located in the northeastern section of the colony, on the
northern side of the road facing it with a ridge. Outbuildings have been
demolished. The house dates from the mid 1800s. It has a log structure
with covered quoins, vertically boarded gables, and a 6-axial ridge
elevation with an entrance in the 3rd axis from the east. The gable
elevation has 2 axes and a 3-axial gable with a rectangular window
enclosed by small rectangular windows. The building is in poor
condition. No. 49 is a house situated in the northern section of
the colony, on the eastern side of the road, facing it with its ridge. It
is a wooden 1.5-storey building dating from ca. 1880. It rests on a high
stone underpinning. The ground floor and an attic room have a
corner-notched log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating
pilaster, while the pointing sill (horizontal planking) and gables
(vertical planking) have a half-timbered structure. The building has a
wooden porch in front of the entrance and a queen post - collar tie roof
structure with an angle brace, and a ceramic roof. The interior has a
two-bay layout (uneven tracts) with a centrally located black kitchen, an
L-shaped hallway, which separates 3 rooms in the northern part of the
house. The gable elevation has 4 axes, a two-level gable with two
rectangular windows enclosed by two rectangular skylights bound by
triangular shapes, and two narrow windows with triangular shapes above.
The western elevation has 7 axes and a shallow 3-axial projection with a
centrally located entrance with a porch. The porch has a rich fretwork
decoration. The pointing sill has small rectangular windows in the axis of
the ground floor windows. There are also two windows in the attic room.
The building is richly decorated with carved planking, a cornice, notched
beams, and original window and door frames. There also is an old
granary/coach house in the yard.
No. 49 is a house situated in the northern section of
the colony, on the eastern side of the road, facing it with its ridge. It
is a wooden 1.5-storey building dating from ca. 1880. It rests on a high
stone underpinning. The ground floor and an attic room have a
corner-notched log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating
pilaster, while the pointing sill (horizontal planking) and gables
(vertical planking) have a half-timbered structure. The building has a
wooden porch in front of the entrance and a queen post - collar tie roof
structure with an angle brace, and a ceramic roof. The interior has a
two-bay layout (uneven tracts) with a centrally located black kitchen, an
L-shaped hallway, which separates 3 rooms in the northern part of the
house. The gable elevation has 4 axes, a two-level gable with two
rectangular windows enclosed by two rectangular skylights bound by
triangular shapes, and two narrow windows with triangular shapes above.
The western elevation has 7 axes and a shallow 3-axial projection with a
centrally located entrance with a porch. The porch has a rich fretwork
decoration. The pointing sill has small rectangular windows in the axis of
the ground floor windows. There are also two windows in the attic room.
The building is richly decorated with carved planking, a cornice, notched
beams, and original window and door frames. There also is an old
granary/coach house in the yard.